Income Inequality: A Debate Over Wealth Redistribution
Income inequality is a pressing issue that has sparked debates globally, raising questions about the wealth distribution and the increasing gap between the rich and the poor. As a small number of billionaires amass extreme wealth, a significant portion of the population struggles to meet even basic needs. This disparity not only threatens social justice but also highlights the necessity for effective philanthropy and wealth redistribution measures. Organizations and individuals alike grapple with the ethical implications of accumulated wealth, particularly when considering the ecological impact of the super-rich. The ongoing discussions surrounding income inequality challenge society to rethink the structures that support both affluence and poverty.
The discussion surrounding financial disparity touches on various concepts such as wealth distribution, economic equity, and the moral responsibilities of the affluent. This discourse often revolves around the extreme fortunes amassed by a select few individuals in our society, raising critical questions about fairness and justice. The dialogue emphasizes the need for a more equitable approach to wealth creation and the mechanisms that could facilitate a fairer society for all citizens. Many advocate for philanthropic efforts aimed at closing the chasm between the wealthy elite and the underprivileged, while others propose systemic changes to create equality of opportunity. As conversations about affluence and its effects continue, the importance of maintaining a balance between wealth accumulation and communal responsibility grows increasingly vital.
The Ethical Dilemmas of Extreme Wealth
Extreme wealth has always provoked complex discussions about morality and ethical responsibility. The concentration of wealth in the hands of a few billionaires raises critical questions regarding the societal implications of such vast wealth. For example, individuals like Elon Musk and Bill Gates are often celebrated for their philanthropic efforts, donating considerable sums to humanitarian causes. Yet, the ethical dilemma lies in whether this philanthropy effectively addresses the systems that cause poverty and inequality in the first place, or if it merely serves as a band-aid, allowing the status quo to persist as billionaires wield greater social influence with their financial resources.
Moreover, the ethical debate extends to how these billionaires accumulate their wealth. The original creation of wealth often relies on market structures that favor specific individuals, fostering an environment where luck and external factors can significantly skew outcomes. This raises fundamental questions about meritocracy and whether it unfairly rewards individuals for traits beyond their control while neglecting the vast majority who remain underprivileged. Reflecting on these themes prompts a deeper inquiry into the moral responsibilities of the rich and the potential need for systemic change, such as wealth redistribution.
Income Inequality: A Ubiquitous Challenge
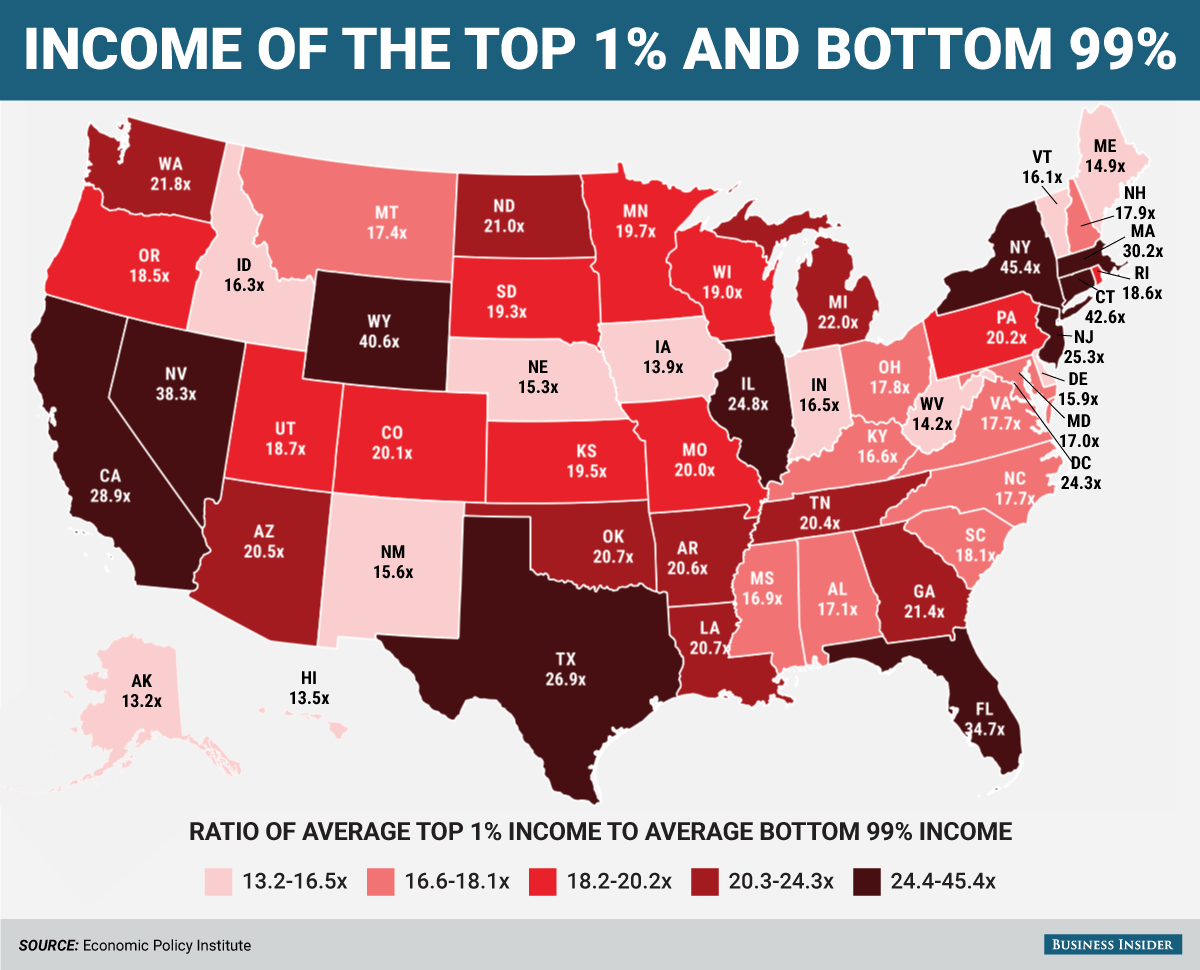
Income inequality stands as one of the most pressing issues in contemporary society, exacerbated by the activities of the wealthiest individuals. With the top 1% accumulating a disproportionate share of resources, the gap between the affluent and the impoverished widens. This inequality is not just a matter of economics; it carries profound social implications, influencing political decisions and access to essential services such as education and healthcare. Critics argue that billionaires leverage their wealth to shape policy in their favor, thereby entrenching a system that perpetuates their wealth while disenfranchising the majority.
Addressing income inequality requires a multi-faceted approach, including redistributive policies that reinvest wealth back into the community. This could involve progressive taxation systems that ensure the wealthy contribute their fair share towards public goods, promoting a more equitable society. Furthermore, empowering grassroots movements advocating for social justice can help amplify the voices of the underprivileged, creating a demand for change. Ultimately, the challenge lies in balancing the economic benefits of a market-driven society with the ethical imperatives of fairness and justice for all.
Philanthropy or Self-Interest? Evaluating Billionaire Contributions
The role of philanthropy among billionaires often finds itself under scrutiny, with some arguing that while charitable donations appear benevolent, they can serve to reinforce existing power structures. For instance, individuals like Mark Zuckerberg and Jeff Bezos invest in various philanthropic initiatives, claiming to address societal challenges such as climate change and poverty. However, critics assert that such acts can also allow billionaires to maintain their wealth while diverting attention from systemic issues, thereby avoiding deeper conversations about necessary structural reform.
Moreover, this dynamic reveals a broader discussion about the effectiveness of philanthropy in driving social change. While these contributions can indeed fund essential projects, they may lack the comprehensive approach required to tackle institutional biases that perpetuate inequality. The question remains: are these philanthropic efforts fostering genuine social justice, or are they merely serving as a means for the wealthy to bolster their images? A shift towards a framework emphasizing participatory governance and community-oriented solutions could enhance the impact of philanthropic endeavors.
Redistribution as a Strategy for Social Justice
Redistribution has emerged as a vital strategy in addressing income inequality and promoting social justice. Advocates argue that redistributing wealth through taxation and social programs can help level the playing field, enabling the underprivileged to gain access to resources and opportunities that would otherwise remain out of reach. This concept resonates deeply within discussions on equity, prompting the need for significant reforms in wealth distribution systems that can effectively improve the lives of the marginalized.
However, the implementation of redistribution strategies often faces resistance. Critics argue that high taxation on billionaires could disincentivize innovation and investment, potentially slowing economic growth. Nevertheless, the societal benefits of redistribution can outweigh such concerns, providing necessary funding for education, healthcare, and community development programs that lift the lower-income brackets. Ultimately, embracing redistribution as a principle not only promotes economic equality but also nurtures a more compassionate and just society.
The Compatibility of Wealth and Progress
The debate on whether extreme wealth can coexist with societal progress continues to polarize opinion. Proponents contend that the wealth generated by billionaires can drive innovation and economic development, citing examples where wealthy individuals have funded groundbreaking research and advancements. This perspective emphasizes that billionaires are not merely net drains on society but can act as catalysts for change, providing resources that can be channeled into socially beneficial projects, especially in technology and renewable energy sectors.
Conversely, critics assert that the wealth accumulation by a select few undermines democratic processes and exacerbates social injustices. As billionaires amass influence over political and economic spheres, there is a risk that their interests take precedence over communal needs, leading to policies that favor the wealthy at the cost of broader public welfare. Balancing the contributions of wealthy individuals with a commitment to democratic principles and social equity remains a challenge that society must navigate carefully.
The Future of Democratic Socialism: Balancing Interests
Democratic socialism presents a compelling framework for navigating income inequality and wealth redistribution. This approach advocates for a political system that promotes social ownership and democratic control of the means of production while ensuring a market economy. By combining the efficiencies of capital markets with social welfare programs, democratic socialism seeks to create a more equitable society where every individual has access to essential services and opportunities for success. Notably, this model can help enhance worker rights, championing a workforce that is empowered rather than exploited.
However, achieving democratic socialism entails significant political transformation and requires widespread public support. Policymakers must navigate the complexities of dismantling entrenched power structures while promoting policies that benefit marginalized communities. By championing policies like universal basic income and expanded labor rights, democratic socialism can address fundamental injustices entrenched by the current economic system. This push for social equity necessitates ongoing dialogue and commitment from all sectors of society, including the wealthiest individuals, to foster a more inclusive and equitable future.
Global Perspectives on Wealth and Inequality
Examining global perspectives on wealth and inequality reveals significant variations in how different cultures and economies address these issues. In countries with relatively low levels of income inequality, such as those in Scandinavia, models of wealth distribution focus on maximizing social welfare through robust public sector programs. These nations illustrate that maintaining high productivity can coexist with policies that prioritize social justice and equality, as they seek to balance market efficiencies with a commitment to lifting the poorest segments of society.
Conversely, nations with stark income disparities often grapple with social unrest and economic instability. In many developing countries, wealth remains concentrated among a small elite, hindering progress towards sustainable development. Addressing wealth inequality on a global scale involves not only national efforts but also international cooperation, as rich nations must play a role in facilitating economic opportunities for those in developing regions. By sharing resources and knowledge, a more equitable global landscape can emerge, fostering growth and prosperity for all.
The Environmental Impact of Extreme Wealth
The environmental implications of extreme wealth also warrant critical examination, particularly considering the significant carbon footprints associated with billionaires. As wealth concentration intensifies, so too does the environmental degradation stemming from the consumption habits of the ultra-rich. Prominent figures in the tech and finance sectors often contribute to climate change through their lavish lifestyles and extensive travel, raising ethical questions about their commitment to sustainability. The juxtaposition of wealth accumulation and environmental responsibility poses challenges not just for billionaires, but for society at large.
Addressing the environmental impact of wealth requires systemic changes that prioritize sustainable practices over mere profit. Advocating for regulations that hold wealthier individuals accountable for their environmental footprints is essential in the fight against climate change. By focusing on green technology and equitable resource distribution, society can create pathways toward sustainable interactions with the environment, challenging the notion that extreme wealth must equate to environmental degradation. Through collaborative efforts, both affluent individuals and communities can work together to mitigate environmental destruction while promoting a healthier planet.
Immigration as a Solution for Poverty Alleviation
One often-overlooked aspect of poverty alleviation involves immigration and the potential benefits it can bring to both individuals and host countries. By enabling individuals from impoverished regions to seek opportunities in wealthier nations, immigration can play a pivotal role in breaking the cycle of poverty. This perspective aligns with arguments that the world’s poorest populations require access to markets where their potential can be realized, contributing to economic growth while simultaneously improving their living standards.
Furthermore, implementing immigration-friendly policies can lead to a more diverse and dynamic labor force, ultimately benefiting host countries economically. As immigrants bring unique skills and perspectives, they can invigorate industries and drive innovation, challenging the barriers posed by income inequality. To recognize immigration as a viable solution to poverty requires a cultural shift towards viewing it as a mutually beneficial arrangement, fostering understanding and collaboration between nations.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does income inequality relate to extreme wealth in society?
Income inequality refers to the uneven distribution of wealth among individuals, often highlighted by the existence of extreme wealth concentrated in the hands of billionaires. This growing gap raises concerns about social justice and the ethical implications of wealth disparity, prompting discussions on the necessity for redistribution of wealth to promote equity.
What role does philanthropy play in addressing income inequality?
Philanthropy is seen by some as a remedy for income inequality, with billionaires like Bill Gates using their wealth to fund initiatives aimed at poverty alleviation and access to education. However, while philanthropy can provide immediate relief, it often sparks debate about the effectiveness of private wealth in achieving systemic change compared to government-led redistribution efforts.
Are billionaires contributing positively to solutions for income inequality?
Billionaires can contribute positively by investing in social programs and innovations that may alleviate poverty. Proponents argue that their wealth can fund initiatives that support the less fortunate and improve overall societal welfare. However, critics argue that the existence of billionaires exacerbates income inequality, suggesting that their wealth could be more effectively redistributed to benefit wider populations.
What are some proposed systems for redistributing wealth to tackle income inequality?
Several proposals for redistributing wealth to address income inequality include implementing progressive taxation, enhancing social safety nets, and supporting policies that promote property-owning democracy. These systems aim to create a more equitable distribution of resources and opportunities while maintaining the benefits of a market economy.
How does income inequality impact social justice initiatives?
Income inequality significantly affects social justice initiatives, as disparities in wealth can lead to unequal access to resources and opportunities. This imbalance challenges the notion of fairness in society, prompting calls for policies aimed at redistributing wealth and ensuring that all individuals, regardless of their economic status, have access to basic rights and resources.
What challenges do we face in addressing extreme wealth and income inequality?
One major challenge in addressing extreme wealth and income inequality is the resistance to taxation and potential government interventions needed for effective redistribution. Furthermore, the influence of wealthy individuals on political processes can hinder reform efforts, as policies may be tailored to protect interests of the super-rich rather than promote equity.
Can individuals in wealthy nations help mitigate global income inequality?
Yes, individuals in wealthy nations can help mitigate global income inequality through direct support for equitable policies, ethical consumerism, and advocacy for immigration reform that allows opportunities for the world’s poorest. Engaging in charitable efforts or community support can also make a significant impact in improving living conditions for those affected by severe poverty.
What is the relationship between billionaires and market forces in reducing income inequality?
Billionaires often operate within market forces that can either exacerbate or alleviate income inequality. While their investments can drive innovation and create jobs, critics argue that such wealth concentration leads to greater systemic inequities. Balancing billionaire contributions with effective governance and equitable policies is crucial in navigating the complex relationship between capital accumulation and social equity.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Extreme Wealth and Environmental Impact | Billionaires, while contributing funds for anti-poverty and green initiatives, disproportionately harm the environment as highlighted by Tom Malleson. |
| Debate on Billionaires’ Role | Panelists argued differing views on whether billionaires are beneficial or harmful to society. |
| Wealth Redistribution | Malleson suggested that wealth redistribution towards green technology would be beneficial. |
| Investment in Poor Countries | Jessica Flanigan defended billionaires by pointing to their investments in countries affected by climate change. |
| Market Economy vs. Central Planning | The discussion highlighted the tension between maintaining a market economy and the potential downsides of central planning. |
| Labor Rights | Malleson referred to the need for labor rights and strong unions as part of proposals for reducing income inequality |
| Property-Owning Democracy | Nien-hê Hsieh proposed a democratic framework that encourages private wealth accumulation while promoting egalitarian property distribution. |
| Immigration as a Solution | Shruti Rajagopalan suggested allowing immigration as a means to alleviate poverty for the world’s poorest. |
Summary
Income inequality is a pressing issue that sparks intense debate about wealth distribution and social justice. The recent discussion at Harvard’s Safra Center for Ethics emphasized the contrasting viewpoints on the roles of billionaires and corporate practices in contributing to or alleviating this inequality. While some argue for the redistribution of wealth, others highlight the potential benefits of billionaires’ investments in innovation and employment. Ultimately, finding a balanced approach that ensures fair economic conditions and environmental sustainability will be crucial in addressing income inequality effectively.